Gitlab and Sql Developer
We recently got access to Gitlab. It is rather more user friendly than our previous Gitolite install, and has lots more features.
One thing I thought might be useful is to connect SQL developer to it and use the IDE features.
The first thing I discovered is that running SQL Developer off a Windows share is a painful business. Also it is likely to be out of date. Installing it locally seems like a good move.
Git requires a Unix like environment in the command line. Particularly as the way Gitlab has been set up means we need to use ssh rather than https to push (Or maybe it is just that is what I understand). Anyway I downloaded git for Windows which seems to work well. It gives a minimal Unix like environment using MinGW. Presumably cygwin will work in the same way if you prefer that.
Once that is installed, you have to create an ssh key pair. I discovered after some googling that the following incantation is required:
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -m PEM -C "psh35@cam.ac.uk"
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/m//.ssh/id_rsa):
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /m//.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /m//.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:O/wmbdpLqDKjvFGKRd601EMeXihm2NSQUBkKRWd2OMA psh35@cam.ac.uk
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
|.+=BOB+.. |
| .E=X*oo |
| oooo= |
| o + . . |
| o + S |
| o o . o |
|. o =.. |
| . .+ ..=+ |
| +o +. .=+. |
+----[SHA256]-----+If the -t rsa -m PEM options aren’t used, the key is in a format which SQL Developer won’t recognise.
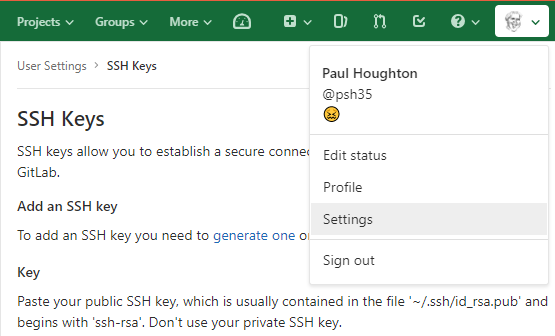
The public key needs to be imported into Gitlab. Cick on your avatar on the top right, and click Settings in the menu that comes up.
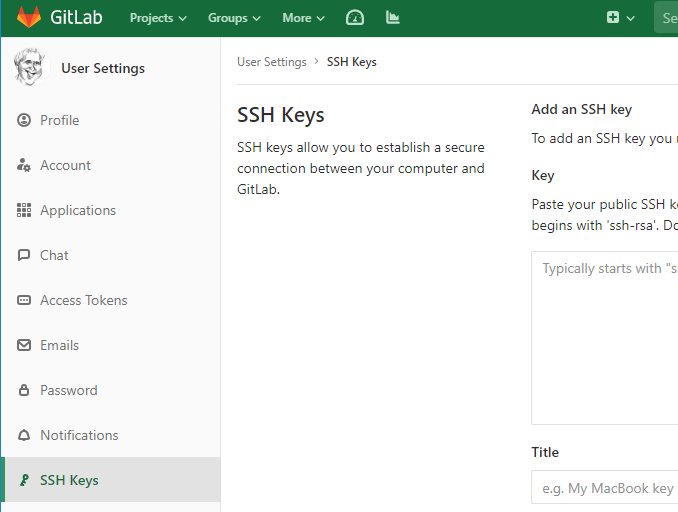
Click on SSH Keys in the left bar, then paste the contents of id_rsa.pub into the large box that appears. The title gets populated from the key, change it so you can recognise it later, then save it by clicking Add key. This can now be used by the git command line.
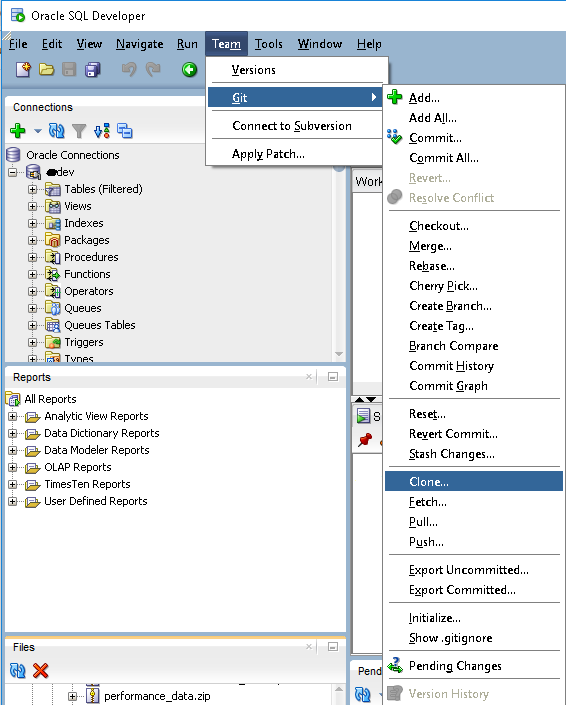
You can clone a remote repository using Team->Git->Clone…
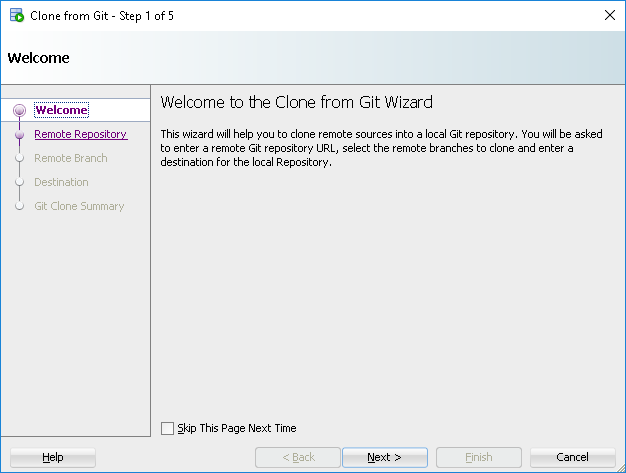
This brings up the clone from GIT wizard. Click next past the welcome screen.
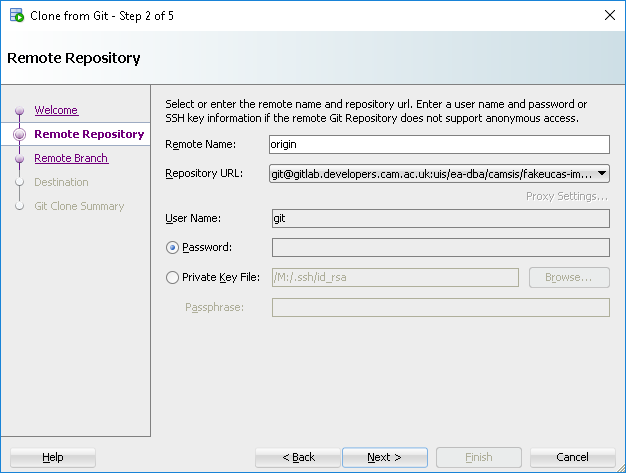
Next enter the repository URL which you can copy from Gitlab. Now, the repository URL has git@ at the front. The remote username is git, or can be left blank as it is in the URL. This confused me for a while! Select the Private Key File option, then browse to the private key that matches the public key that was uploaded (id_rsa).
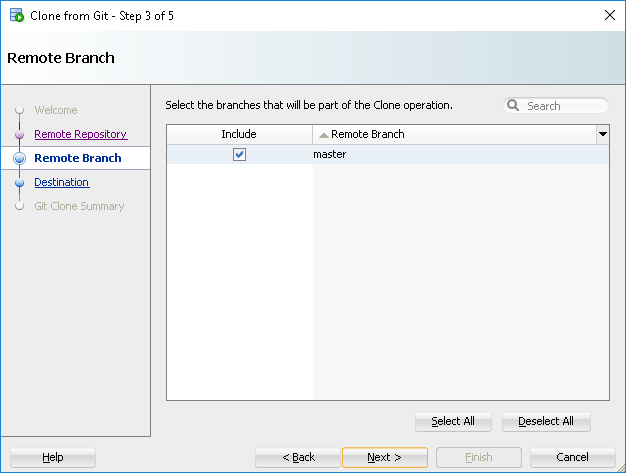
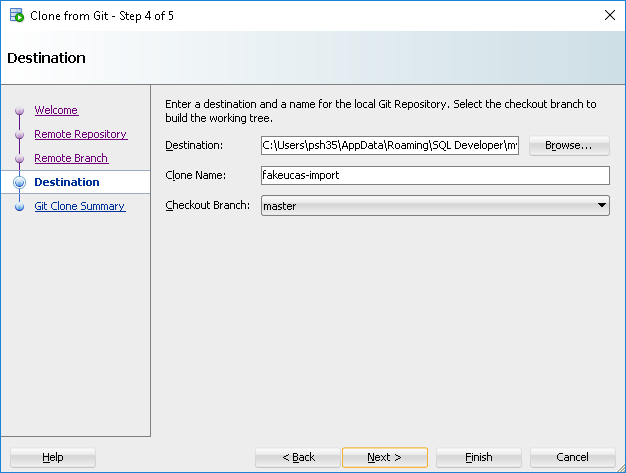
Click next, then select the branch you would like (I just have Master) Lastly select the destination, optionally view the summary, then click finish to actually do the clone.
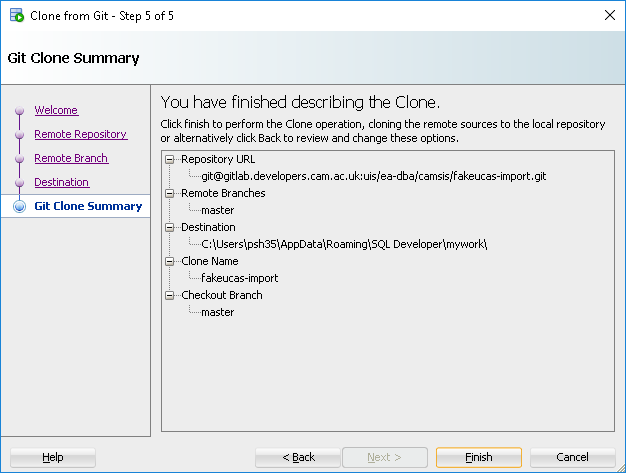
Select View-> Files from the SQL Developer menu. A file tree is displayed. Browse to the cloned repository, and files can be opened in the editor by douhle clicking. Right click on a file and the Versioning submenu can be used to perform all the usual git tasks.